Vertigo is the sensation that either your body or your environment is moving (usually spinning). Vertigo can be a symptom of many different illnesses and disorders. The most common causes of vertigo are illnesses that affect the inner ear, including:
• Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo — In this condition, a change in head position causes a sudden sensation of spinning. The most likely cause is small crystals that break loose in the canals of the inner ear and touch the sensitive nerve endings inside.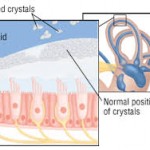
• Acute labyrinthitis, also called vestibular neuritis — This is an inflammation of the balance apparatus of the inner ear, probably caused by a viral infection. 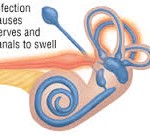
• Ménière’s disease — This causes repeat episodes of dizziness, usually with ringing in the ear and progressive low-frequency hearing loss. Ménière’s disease is caused by a change in the volume of fluid inside the inner ear. Although the reason for this change is unknown, scientists suspect that it may be linked to loud noise, to a viral infection or to biologic factors inside the ear itself.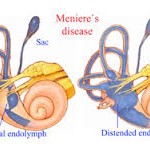
Symptoms
Vertigo can feel like the room is spinning or like you are spinning in the room, or it can be just a sense of imbalance. It may be associated with nausea, vomiting and ringing in one or both ears (tinnitus).
Diagnosis
Doctor will diagnose vertigo based on patient’s description of what he/she is feeling. Vertigo can be divided into two major categories, peripheral vertigo and central vertigo.
Peripheral vertigo: Is much more common, includes benign positional vertigo, labyrinthitis and Ménière’s disease. Positional vertigo is diagnosed when moving the head causes the vertigo and returning the head to a neutral position relieves symptoms. Labyrinthitis and Ménière’s attacks usually come on abruptly and last from a few hours to a couple of days. There may be intense nausea and vomiting and variable hearing loss.
Central vertigo: Is a more serious problem in the cerebellum (back part of the brain) or brain stem.
Doctor will evaluate patient’s eye to look for abnormal jerking movements (nystagmus). The pattern of eye movements may help to determine if the problem is peripheral or central. Usually, no further testing is needed unless doctor suspects he/she have central vertigo. If central vertigo is suspected, doctor will order a computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brain.
Expected Duration
Depending on its cause, vertigo may last only a few seconds or last for weeks or months.
Prevention
Vertigo can happen to anyone, and there is no way to prevent the first episode. Because vertigo can be associated with an intense sense of imbalance, it is important to avoid situations in which a fall could cause significant harm, like climbing a ladder or working on a slanted roof.
Treatment
Homeopathic medicines are selected according to symptoms. Patient need to see a homeopathic doctor for a proper homeopathic medicine.
Prognosis
Most cases of vertigo last a few hours to a few days. Symptoms caused by acute labyrinthitis almost always go away without permanent injury. Other causes of vertigo may result in symptoms that are more persistent.
Comments (0)